
Squadron, commanded by Union Flag Officer David Glasgow Farragut, fought past Confederate Forts Jackson and St. 10 in the Mississippi River, seized MemphisĮntering the mouth of the Mississippi River, the ships of the West Gulf Blockading Continuing theirĪdvance, the Federals gained victory in the bloody battle at Shiloh in April, at Corinth in May, and having forced the surrender of Island No. Henry and Donelson, opening the pathway for invasion of the Deep South. Moving along the Tennessee and Cumberland rivers, Union forces seized Forts The initial engagement at Belmont, Missouri, provided valuable experienceįor Grant who became the most important Union general of the war. Mississippi River valley from the Confederates. Plan by simultaneously heading south from Paducah, Kentucky, and north from the Gulf of Mexico to wrest control of the lower Late in 1861, Union land and naval forces launched a key element of the Anaconda That broke southern earth, northerners built the steamboats that shipped southern crops, and northerners purchased the final Relied on northern factories for everything it needed to grow, refine, and market its crops. The South was dependent on a plantation economy for its livelihood, but it also Southerners feared this change would forever rob them of their way of life.Īgriculture was the foundation of the economy of America, but its practice varied between the North and the
#Civil war anaconda plan free
Kansas-Nebraska Act in 1854, which allowed territories to decide whether to become free or slave states , Over the years, compromises maintained a delicate balance in Congress between free and slave states. Regional economic and cultural diversity controlled national politics. Scott's plan called for blockading the southern coast and a driveĭown the Mississippi River to cut the Confederacy in two. Of the Mississippi River in the overall strategy of the war. His strategy, known as the "Anaconda Plan," reflected the importance History of the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indian NationĬherokee War Rituals, Culture, Festivals, Government, and BeliefsĬivil War Diary, Memoirs, Letters, and NewspapersĮarly in the war, Union General Winfield Scott envisioned a broad sweeping plan to crush the rebellion. North Carolina: American Civil War PhotosĬherokee Indian Heritage, History, Culture, Customs, Ceremonies, and Religion Western North Carolina: Civil War Troops, Regiments, Units Western North Carolina and the American Civil War North Carolina Civil War Regiments and Battles North Carolina Civil War History and Battles North Carolina American Civil War Statistics, Battles, History Organization of Union and Confederate Armies: Infantry, Cavalry, ArtilleryĬivil War Navy: Union Navy and Confederate NavyĪmerican Civil War: Casualties, Battles and BattlefieldsĬivil War Casualties, Fatalities & StatisticsĪmerican Civil War Desertion and Deserters: Union and ConfederateĬivil War Prisoner of War: Union and Confederate Prison HistoryĬivil War Reconstruction Era and AftermathĪmerican Civil War Genealogy and ResearchĪmerican Civil War Pictures - PhotographsĪfrican Americans and American Civil War History These men used a version of the Anaconda Plan to eventually win the war against the Confederacy.Anaconda Plan Civil War Winfield Scott Anaconda Plan GeneralĬauses of the Civil War : What Caused the Civil War Though the Plan was rejected, it was later revisited by Ulysses S. This would secure the river down to the naval blockade, dividing the South in half and establishing communications lines between the ships and the North. The Anaconda Plan would move 60,000 Union soldiers in 40 steamboats and 20 gunboats down the Mississippi River, capturing forts and towns along the way. While the North was very industrialized and relied on railroads, the South still primarily used boats. This river was the main transportation method in the South. The economy would be crippled, and the Confederacy would soon run out of resources.
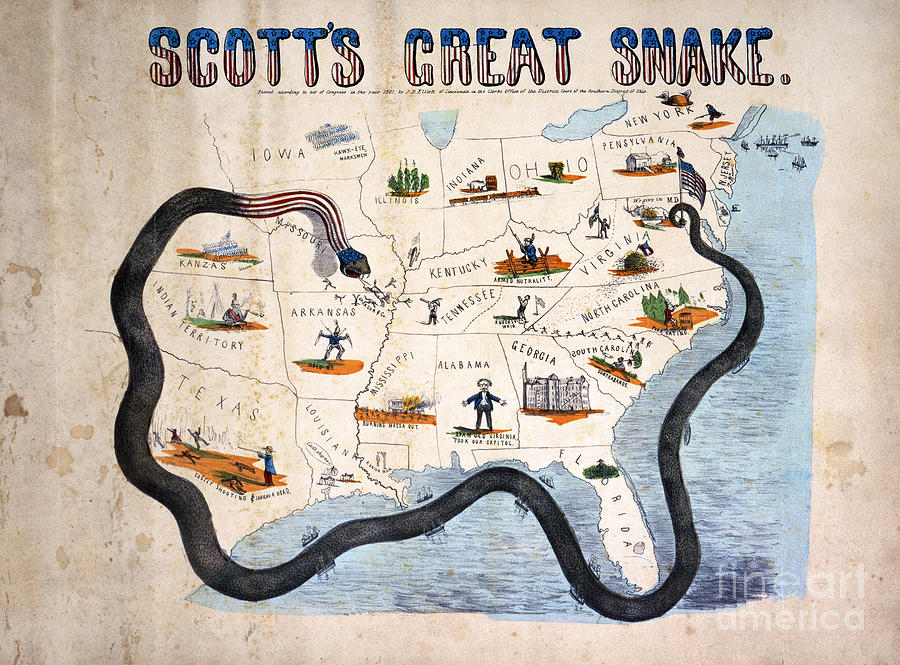

in doing so, the South's trade would be cut off. The Anaconda Plan hoped to establish a naval blockade on the Confederacy's Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico ports. The South relied heavily on trade with European powers, particularly Britain and France. There were two basic objectives, as can be seen in the image. They preferred to crush the South with the North's sheer numbers, as opposed to the Anaconda Plan, which would minimize losses but required patience. The strategy was never fully implemented, as Scott's fellow generals thought it was too passive. The plan would isolate the South from the outside world, preventing trade, limiting transportation, and reducing resources. At the beginning of the war, General Winfield Scott designed the Anaconda Plan to achieve a Union win.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
